Page 408 - The Vasculitides, Volume 1: General Considerations and Systemic Vasculitis
P. 408
382 Rami N. Al-Rohil and J. Andew Carlson
Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis
Clinicopathologically typified by granulomatous inflammation of the upper and lower
respiratory tracts (Figures 12, 13) and necrotizing granulomatous inflammation of the kidneys
leading to glomerulonephritis [18]. The disease is not evenly distributed among geographic
areas, time intervals or ethnic populations [26]. The diagnosis is based upon biopsy and
surrogate markers of granulomatous inflammation of the respiratory tract and kidney,
systemic necrotizing vasculitis of small-to medium-sized vessels, with positive c-ANCA
serology, but without eosinophilia in blood and biopsy tissue sample. About 10% to 40% of
patients with GPA develop cutaneous disease during the course of disease [27-29] that can
takes one of many forms including, palpable and non-palpable purpura due to small vessel
neutrophilic vasculitis; subcutaneous nodules, ulcers and digital infarcts with gangrene due to
medium vessel vasculitis; polymorphic lesions consisting of rheumatoid papules and nodules
which are necrotic over extensor surfaces particularly the elbows; and pyoderma
gangrenosum-like ulcers and gingival hyperplasia with strawberry gingivitis. Among 40
patients with the diagnosis of GPA, Patten and colleagues [27] noted that 16 (40%) patients
had cutaneous and oral mucosal disease in whom 12 had only skin disorder most commonly
palpable purpura, 2 had oral mucosal disease, and 2 had both skin and mucosal disease
leading to oral ulcers and a single example of gingival hyperplasia.
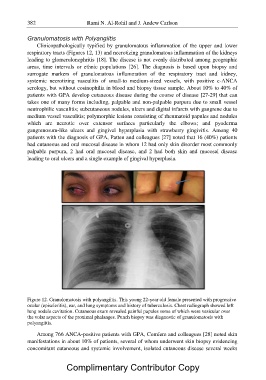
Figure 12. Granulomatosis with polyangiitis. This young 22-year old female presented with progressive
ocular (episcleritis), ear, and lung symptoms and history of tuberculosis. Chest radiograph showed left
lung nodule cavitation. Cutaneous exam revealed painful papules some of which were vesicular over
the volar aspects of the proximal phalanges. Punch biopsy was diagnostic of granulomatosis with
polyangiitis.
Among 766 ANCA-positive patients with GPA, Comfere and colleagues [28] noted skin
manifestations in about 10% of patients, several of whom underwent skin biopsy evidencing
concomitant cutaneous and systemic involvement, isolated cutaneous disease several weeks
Complimentary Contributor Copy