Page 309 - The Vasculitides, Volume 1: General Considerations and Systemic Vasculitis
P. 309
Systemic Vasculitis of the Gastrointestinal Tract 283
While clinically evident mesenteric involvement in uncommon, occult radiographic
manifestations were noted on arteriography in 18% of patients with GCA [4, 37, 38].
Of 11 patients with bowel involvement in GCA, nine were biopsy-proven [4, 7, 39-46],
of whom four presented with abdominal symptoms in the absence of symptoms of temporal
arteritis. Temporal artery biopsy was positive in only two of the four patients suggesting a
negative temporal artery biopsy was unable to reliably exclude GCA involving the mesenteric
vasculature [4].
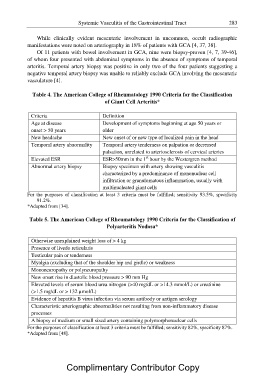
Table 4. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 Criteria for the Classification
of Giant Cell Arteritis*
Criteria Definition
Age at disease Development of symptoms beginning at age 50 years or
onset > 50 years older
New headache New onset of or new type of localized pain in the head
Temporal artery abnormality Temporal artery tenderness on palpation or decreased
Elevated ESR pulsation, unrelated to arteriosclerosis of cervical arteries
ESR>50mm in the 1st hour by the Westergren method
Abnormal artery biopsy Biopsy specimen with artery showing vasculitis
characterized by a predominance of mononuclear cell
infiltration or granulomatous inflammation, usually with
multinucleated giant cells
For the purposes of classification at least 3 criteria must be fulfilled; sensitivity 93.5%, specificity
91.2%.
*Adapted from [34].
Table 5. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 Criteria for the Classification of
Polyarteritis Nodosa*
Otherwise unexplained weight loss of > 4 kg
Presence of livedo reticularis
Testicular pain or tenderness
Myalgia (excluding that of the shoulder hip and girdle) or weakness
Mononeuropathy or polyneuropathy
New onset rise in diastolic blood pressure > 90 mm Hg
Elevated levels of serum blood urea nitrogen (>40 mg/dL or >14.3 mmol/L) or creatinine
(>1.5 mg/dL or > 132 µmol/L)
Evidence of hepatitis B virus infection via serum antibody or antigen serology
Characteristic arteriographic abnormalities not resulting from non-inflammatory disease
processes
A biopsy of medium or small sized artery containing polymorphonuclear cells
For the purposes of classification at least 3 criteria must be fulfilled; sensitivity 82%, specificity 87%.
*Adapted from [48].
Complimentary Contributor Copy