Page 110 - The Vasculitides Volumes 2
P. 110
86 Aleksandra Mineyko and Adam Kirton
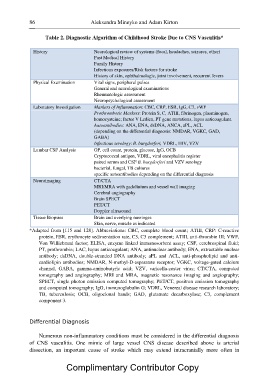
Table 2. Diagnostic Algorithm of Childhood Stroke Due to CNS Vasculitis*
History Neurological review of systems (focal, headaches, seizures, other)
Past Medical History
Family History
Infectious exposures/Risk factors for stroke
History of skin, ophthalmologic, joint involvement, recurrent fevers
Physical Examination Vital signs, peripheral pulses
General and neurological examinations
Rheumatologic assessment
Neuropsychological assessment
Laboratory Investigation Markers of Inflammation: CBC, CRP, ESR, IgG, C3, vWF
Prothrombotic Markers: Protein S, C, ATIII, fibrinogen, plasminogen,
homocysteine; factor V Ledien, PT gene mutations, lupus anticoagulant.
Autoantibodies: ANA, ENA, dsDNA, ANCA, aPL, ACL
(depending on the differential diagnosis: NMDAR, VGKC, GAD,
GABA)
Infectious serology: B. burgdorferi, VDRL, HIV, VZV
Lumbar CSF Analysis OP, cell count, protein, glucose, IgG, OCB
Cryptococcal antigen, VDRL, viral encephalitis register
paired serum and CSF B. burgdorferi and VZV serology
bacterial, fungal, TB cultures
specific autoantibodies depending on the differential diagnosis
Neuroimaging CT/CTA
MRI/MRA with gadolinium and vessel wall imaging
Cerebral angiography
Brain SPECT
PET/CT
Doppler ultrasound
Tissue Biopsies Brain and overlying meninges
Skin, nerve, muscle as indicated
*Adapted from [115 and 128]. Abbreviations: CBC, complete blood count; ATIII, CRP: C-reactive
protein, ESR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C3, C3 complement; ATIII, anti-thrombin III; VWF,
Von Williebrand factor; ELISA, enzyme linked immunosorbent assay; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid;
PT, prothrombin; LAC, lupus anticoagulant; ANA, antinuclear antibody; ENA, extractable nuclear
antibody; dsDNA, double-stranded DNA antibody; aPL and ACL, anti-phospholipid and anti-
cardiolipin antibodies; NMDAR, N-methyl-D-asparatate receptor; VGKC, voltage-gated calcium
channel, GABA, gamma-aminobutyric acid; VZV, varicella-zoster virus; CT/CTA, computed
tomography and angiography; MRI and MRA, magnetic resonance imaging and angiography;
SPECT, single photon emission computed tomography; PET/CT, positron emission tomography
and computed tomography; IgG, immunoglobulin G; VDRL, Venereal disease research laboratory;
TB, tuberculosis; OCB, oligoclonal bands; GAD, glutamate decarboxylase; C3, complement
component 3.
Differential Diagnosis
Numerous non-inflammatory conditions must be considered in the differential diagnosis
of CNS vasculitis. One mimic of large vessel CNS disease described above is arterial
dissection, an important cause of stroke which may extend intracranially more often in
Complimentary Contributor Copy