Page 384 - The Vasculitides, Volume 1: General Considerations and Systemic Vasculitis
P. 384
358 Sarah Conway and David S. Younger
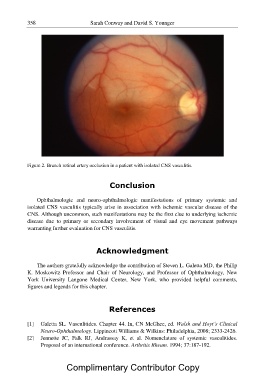
Figure 2. Branch retinal artery occlusion in a patient with isolated CNS vasculitis.
Conclusion
Ophthalmologic and neuro-ophthalmologic manifestations of primary systemic and
isolated CNS vasculitis typically arise in association with ischemic vascular disease of the
CNS. Although uncommon, such manifestations may be the first clue to underlying ischemic
disease due to primary or secondary involvement of visual and eye movement pathways
warranting further evaluation for CNS vasculitis.
Acknowledgment
The authors gratefully acknowledge the contribution of Steven L. Galetta MD, the Philip
K. Moskowitz Professor and Chair of Neurology, and Professor of Ophthalmology, New
York University Langone Medical Center, New York, who provided helpful comments,
figures and legends for this chapter.
References
[1] Galetta SL. Vasculitides. Chapter 44. In, CN McGhee, ed. Walsh and Hoyt’s Clinical
Neuro-Ophthalmology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, 2008; 2333-2426.
[2] Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Andrassay K, et al. Nomenclature of systemic vasculitides.
Proposal of an international conference. Arthritis Rheum. 1994; 37:187-192.
Complimentary Contributor Copy